【学习参考资料】:菜鸟教程-Java教程
1,Java基本数据类型
变量就是申请内存来存储值。内存管理系统根据变量的类型为变量分配存储空间,分配的空间只能用来储存该类型数据。
Java有两大数据类型:内置数据类型和引用数据类型。
1)内置数据类型
| 名称 | 描述 | 取值范围 | 默认值 | 主要用途 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| byte | 8位,有符号的,以二进制补码表示的整数 | - $2^7$ ~ $2^7$ -1 | 0 | 在大型数组中节约空间,代替整数 |
| short | 16位,有符号的,以二进制补码表示的整数 | -$2^{15}$~$2^{15}$-1 | 0 | 节省空间 |
| int | 32位,有符号的,以二进制补码表示的整数 | -$2^{31}$~$2^{31}$-1 | 0 | 整型变量的默认类型 |
| long | 64位,有符号的,以二进制补码表示的整数 | -$2^{63}$~$2^{63}$-1 | 0L | 使用在需要比较大整数的系统上 |
| float | 单精度、32位、符合IEEE 754标准的浮点数 | -$2^{31}$~$2^{31}$-1 | 0.0f | 在存储大型浮点数组时可以节省空间;不能用来表示精确的值 |
| double | 双精度、64位、符合IEEE 754标准的浮点数 | -$2^{63}$~$2^{63}$-1 | 0.0d | 浮点数变量的默认类型 |
| boolean | 表示一位的信息 | true,false | false | 作为一种标记来记录true/false情况 |
| char | 单一的 16 位 Unicode 字符 | \u0000~\uffff(0~$2^{16}$-1) |
存储任何字符 |
2)引用类型
- 在Java中,引用类型的变量非常类似于
C/C++的指针。引用类型指向一个对象,指向对象的变量是引用变量。- 对象、数组都是引用数据类型。
- 所有引用类型的默认值都是
null。- 一个引用变量可以用来引用与任何与之兼容的类型。
3)Java常量:常量在程序运行时,不会被修改,关键字final。通常使用大写字母表示常量。
4)Java类型转换
自动类型转换:转换从低级到高级。
- 数据类型转换满足的
原则:
(1)不能对boolean类型进行类型转换;
(2)不能把对象类型转换成不相关类的对象;
(3)在把容量大的类型转换为容量小的类型时必须使用强制类型转换;
(4)转换过程中可能导致溢出或损失精度;
(5)浮点数到整数的转换是通过舍弃小数得到,而不是四舍五入。强制类型转换:条件是转换的数据类型必须是兼容的。隐含强制类型转换
2,Java语句类型
1)循环结构
whiledo...whileforforeach增强型for循环:主要用于数组- demo:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public static void main(String args[]){
int [] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for(int x : numbers ){
System.out.print( x );
System.out.print(",");
}
System.out.print("\n");
String [] names ={"James", "Larry", "Tom", "Lacy"};
# 增强型for循环
for( String name : names ) {
System.out.print( name );
System.out.print(",");
}
}
}
2)break语句:主要用于循环语句或者switch语句中;跳出最里层的循环,并且继续执行该循环下面的语句。
3)continue语句:适用于任何循环控制结构中,作用是让程序立刻跳转到下一次循环的迭代。
4)分支结构
if:一个if语句包含一个布尔表达式和一条或多条语句。switch case语句:判断一个变量与一系列值中某个值是否相等,每个值称为一个分支。
3,Java基础类
1)Number & Math类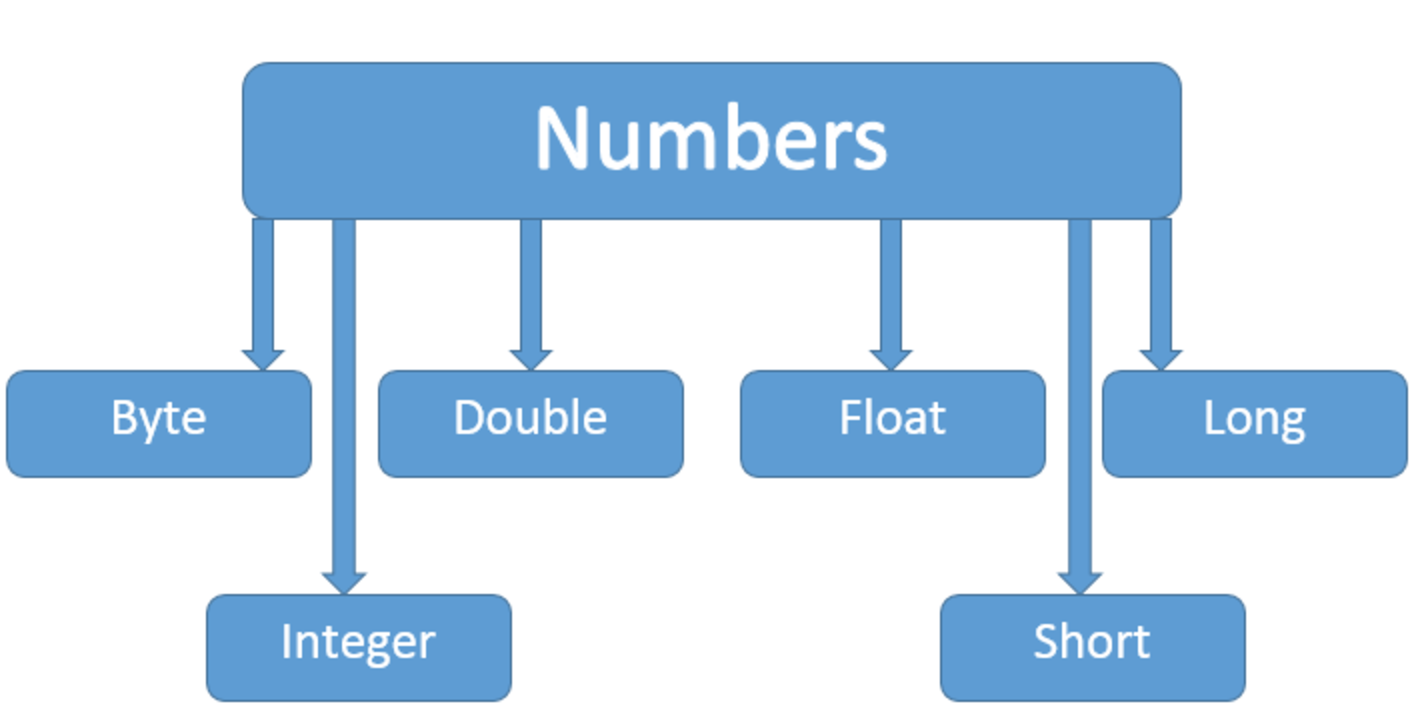
2)Math类:包含了用于执行基本数学运算的属性和方法,如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数。
3)Character类:对单个字符进行操作。
将一个char类型的参数传递给需要一个Character类型参数的方法时,那么编译器会自动地将char类型参数转换为Character对象。 这种特征称为装箱,反过来称为拆箱。
4)String类
用于获取有关对象的信息的方法称为访问器方法。
5)StringBuffer和StringBuilder类
- 和
String类不同的是,StringBuffer和StringBuilder类的对象能够被多次的修改,并且不产生新的未使用对象。StringBuilder类在Java 5中被提出,它和StringBuffer之间的最大不同在于StringBuilder的方法不是线程安全的(不能同步访问)。- 由于
StringBuilder相较于StringBuffer有速度优势,所以多数情况下建议使用StringBuilder类。- 在应用程序要求线程安全的情况下,则必须使用
StringBuffer类。
4,Java数组
1)声明数组1
2
3dataType[] arrayRefVar; // 首选的方法
# or
dataType arrayRefVar[]; // 效果相同,但不是首选方法
2)创建数组
1
arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];
3)多维数组1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11type[][] typeName = new type[typeLength1][typeLength2]; // 直接为每一维分配空间
// 从最高维开始,分别为每一维分配空间
String s[][] = new String[2][];
s[0] = new String[2];
s[1] = new String[3];
s[0][0] = new String("Good");
s[0][1] = new String("Luck");
s[1][0] = new String("to");
s[1][1] = new String("you");
s[1][2] = new String("!");
4)Arrays类java.util.Arrays 类能方便地操作数组,它提供的所有方法都是静态的。具有以下功能:
- 给数组赋值:通过 fill 方法。
- 对数组排序:通过 sort 方法,按升序。
- 比较数组:通过 equals 方法比较数组中元素值是否相等。
- 查找数组元素:通过 binarySearch 方法能对排序好的数组进行二分查找法操作。
5,Java日期时间
java.util包提供了Date类来封装当前的日期和时间。 Date类提供两个构造函数来实例化 Date 对象。
第一个构造函数使用当前日期和时间来初始化对象。1
Date( )
第二个构造函数接收一个参数,该参数是从1970年1月1日起的毫秒数。1
Date(long millisec)
1)获取当前日期时间1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8import java.util.Date;
public class DateDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date.toString());
}
}
2)日期比较
getTime():获取两个日期(自1970年1月1日经历的毫秒数值),然后比较这两个值。before(),after(),equals()compareTo():由Comparable接口定义的,Date类实现了这个接口。
3)格式化日期时间
SimpleDataFormat1
2
3
4
5
6
7public class DateTestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date now = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat ft = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("当前时间为:"+ft.format(now));
}
}
printf1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public class DateTestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date now = new Date();
//c的使用
System.out.printf("全部日期和时间信息:%tc%n", now);
//f的使用
System.out.printf("年-月-日格式:%tF%n", now);
//d的使用
System.out.printf("月/日/年格式:%tD%n", now);
//r的使用
System.out.printf("HH:MM:SS PM格式(12时制):%tr%n", now);
//t的使用
System.out.printf("HH:MM:SS格式(24时制):%tT%n", now);
//R的使用
System.out.printf("HH:MM格式(24时制):%tR", now);
}
}
4)Java休眠(Sleep)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class SleepDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println(new Date()+"\n");
Thread.sleep(1000*5);
System.out.println(new Date()+"\n");
} catch (Exception ex){
System.out.println("Got an exception: "+ex);
}
}
}
5)Calendar类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public class DateTestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个代表系统当前日期的Calendar对象
Calendar now = Calendar.getInstance();
int year = now.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = now.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int day = now.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
int date = now.get(Calendar.DATE);
int hour = now.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
int minute = now.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
int second = now.get(Calendar.SECOND);
System.out.println(now.getTime());
System.out.printf("%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d\n%d\n",
year, month, day, hour, minute, second, date);
// 创建一个表示2009年3月12日的Calendar对象
now.set(2009, 3-1, 12);
System.out.println(now.getTime());
}
}
6)GregorianCalendar类:实现了公历日历,是Calendar类的一个具体实现。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class DateTestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GregorianCalendar gCalender = new GregorianCalendar();
int year = gCalender.get(Calendar.YEAR);
if (gCalender.isLeapYear(year)) {
System.out.println("当前年份是闰年!");
} else {
System.out.println("当前年份不是闰年!");
}
}
}
6,正则表达式
1) java.util.regex包主要包括以下三个类:
Pattern类:是一个正则表达式的编译表示。Pattern类没有公共构造方法。要创建一个Pattern对象,你必须首先调用其公共静态编译方法,它返回一个Pattern对象。该方法接受一个正则表达式作为它的第一个参数。Matcher类:是对输入字符串进行解释和匹配操作的引擎。PatternSyntaxException:是一个非强制异常类,它表示一个正则表达式模式中的语法错误。
1 | public class RegexDemo { |
2)捕获组捕获组是把多个字符当一个单独单元进行处理的方法,它通过对括号内的字符分组来创建。特殊的组(group(0)),它总是代表整个表达式。该组不包括在 groupCount 的返回值中。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public class RegexDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "I am a student, graduated from HuBei University in 2013. ";
String pattern = "(\\D*)(\\d+)(.*)";
// 创建Pattern对象
Pattern rex = Pattern.compile(pattern);
// 创建matcher对象
Matcher matcher = rex.matcher(content);
if (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("Found value: " + matcher.group(0));
System.out.println("Found value: " + matcher.group(1));
System.out.println("Found value: " + matcher.group(2));
System.out.println("Found value: " + matcher.group(3));
} else {
System.out.println("No match!!!");
}
}
}
7,Java方法
1)Java方法定义:Java方法是语句的集合,他们在一起执行一个功能。
- 方法是解决一类问题的步骤的有序组合
- 方法包含于类或对象中
- 方法在程序中被创建,在其他地方被引用
2)Java方法的优点
- 使程序变得更简短而清晰
- 有利于程序维护
- 可以提高程序开发的效率
- 提高了代码的重用性
3)Java方法的命名规则
- 必须以
字母、'_'或'$'开头(方法名第一个单词应以小写字母开头,后面的单词则用大写字母开头写,不使用连接符);- 可以包括数字,但不能以它开头;
- 下划线可能出现在
JUnit测试方法名称中用以分隔名称的逻辑组件。
4)Java方法的定义1
2
3
4
5
6修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型 参数名){
...
方法体
...
return 返回值;
}
5)Java方法调用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public class MaxTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 2, j = 4;
int max = getMax(i, j);
System.out.printf("%d和%d比较,最大值是:%d.", i, j, max);
}
private static int getMax(int num1, int num2) {
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}
}
6)void关键字
7)Java方法重载:一个类的两个方法拥有相同的名字,但是有不同的参数列表。
8)变量作用域
9)命令行参数:命令行参数是在执行程序时候紧跟在程序名字后面的信息。
10)构造方法:当一个对象被创建时候,构造方法用来初始化该对象。构造方法和它所在类的名字相同,但构造方法没有返回值。
11)可变参数:JDK1.5开始,Java支持传递同类型的可变参数给一个方法。1
typeName... parameterName
- 在方法声明中,在指定参数类型后加一个省略号(
...) 。 - 一个方法中只能指定一个可变参数,它必须是方法的最后一个参数。任何普通的参数必须在它之前声明。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public class MaxTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double max = getMax(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 0, 1);
System.out.printf("...numbers中,最大值是:%.2f.", max);
}
private static double getMax(double... numbers) {
if (numbers.length == 0) {
System.out.println("No argument passed.");
return -10000000000L;
}
double result = numbers[0];
for (double var: numbers) {
if (var > result) {
result = var;
}
}
return result;
}
}
12)finalize()方法:在对象被垃圾收集器析构(回收)之前调用,用来清除回收对象。
Java 的内存回收可以由 JVM 来自动完成。- FinalizationDemo.java如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23public class FinalizationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cake c1 = new Cake(1);
Cake c2 = new Cake(2);
Cake c3 = new Cake(3);
c2 = c3 = null;
System.gc(); // 调用Java垃圾回收集器
}
}
class Cake extends Object {
private int id;
public Cake(int id) {
this.id = id;
System.out.println("Cake Object " + id + " is created.");
}
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
super.finalize();
System.out.println("Cake object " + id + " is disposed.");
}
}
8,Java流(Stream),文件(File)和IO
Java.io包几乎包含了所有操作输入、输出需要的类。
一个流可以理解为一个数据的序列。输入流表示从一个源读取数据,输出流表示向一个目标写数据。
1)读取控制台输入:Java的控制台输入由System.in完成。1
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
2)从控制台读取多字符输入:从BufferedReader对象读取一个字符要使用 read()方法。1
int read() throws IOException
- BRReadLine.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class BRReadLine {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
char ch;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("输入字符,按下'q'键退出.");
do {
ch = (char) br.read();
System.out.println(ch);
} while (ch != 'q');
}
}
3)从控制台读取字符串:从 标准输入读取一个字符要使用BufferedReader的 readLine()方法。1
String readLine() throws IOException
- BRReadLines.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public class BRReadLines {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Enter lines of text;");
System.out.println("Enter 'end' to quit.");
do {
str = br.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
} while (!str.equals("end"));
}
}
4)控制台输出:控制台的输出由 print() 和 println() 完成。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class WriteDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num;
num = 'A';
System.out.write(num);
System.out.write('\n');
}
}
5)读写文件:一个流被定义为一个数据序列。输入流用于从源读取数据,输出流用于向目标写数据。
6)FileInputStream:该流用于从文件读取数据,它的对象可以用关键字new来创建。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25/**
* 把给定的context以二进制写进文件,同时输出控制台
* 但是存在乱码问题
*/
public class FileStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try {
byte[] bWrite = {'a', 11, 21, 32, 40, 54};
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("file_test.txt");
for (byte var: bWrite) {
os.write(var);
}
os.close();
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("file_test.txt");
int size = is.available();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.println((char) is.read() + " ");
}
is.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println("File InputStream error: " + ex.toString());
}
}
}
7)FileOutputStream:该流用来创建一个文件并向文件中写数据,它的对象可以用关键字 new 来创建。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35/**
* 把给定的context以二进制写进文件,同时输出控制台
*/
public class FileIOStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("file_test.txt");
// 构建FileOutputStream对象,文件不存在会自动新建
FileOutputStream fop = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 构建对象,参数可以指定编码,默认为操作系统默认编码,windows是gbk
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fop, "UTF-8");
// 写入到缓冲区
writer.append("中文输入");
writer.append("\r\n");
writer.append("English input");
// 关闭写入流,同时会把缓冲区的内容写入文件
writer.close();
// 关闭输出流,释放系统资源
fop.close();
FileInputStream fip = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(fip, "UTF-8");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (reader.ready()) {
sb.append((char) reader.read());
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
reader.close();
fip.close();
}
}
- 关于文件和
I/O的一些其他类:File Class;FileReader Class;FileWriter Class。
9,Java中的目录
1)创建目录File类中有两个方法可以用来创建文件夹:
mkdir( )方法创建一个文件夹,成功则返回true,失败则返回false。mkdirs()方法创建一个文件夹和它的所有父文件夹。
1 | public class CreateDir { |
2)读取目录1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public class ReadDir {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String dirName = "/home/share";
File fp = new File(dirName);
if (fp.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("目录:" + dirName);
// 提取包含的文件和文件夹的列表
String[] strings = fp.list();
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
File tmp = new File(dirName + "/" + strings[i]);
if (tmp.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println(strings[i] + " 是一个目录.");
} else {
System.out.println(strings[i] + " 是一个文件.");
}
}
} else {
System.out.println(dirName + " 不是一个目录.");
}
}
}
3)删除目录或文件:删除文件可以使用java.io.File.delete()方法。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public class DeleteDir {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File folder = new File("/home/share/java");
deleteFolder(folder);
}
// 删除文件及目录
private static void deleteFolder(File folder) {
File[] files = folder.listFiles();
if (files != null) {
for (File fp: files) {
if (fp.isDirectory()) {
deleteFolder(fp);
} else {
fp.delete();
}
}
}
folder.delete();
}
}
10,Java Scanner类
java.util.Scanner 是 Java5 的新特征,我们可以通过 Scanner 类来获取用户的输入。基本语法如下:1
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
1)使用next方法
- 一定要读取到有效字符后才可以结束输入。
- 对输入有效字符之前遇到的空白,
next()方法会自动将其去掉。- 只有输入有效字符后才将其后面输入的空白作为分隔符或者结束符。
next()不能得到带有空格的字符串。
- ScannerNext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public class ScannerNext {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Next方式接收:");
// 判断是否还有输入
if (scan.hasNext()) {
String str = scan.next();
System.out.println("输入的数据为:" + str);
}
scan.close();
}
}
2)使用nextLine方法
- 以Enter为结束符,也就是说 nextLine()方法返回的是输入回车之前的所有字符。
- 可以获得空白。
- ScannerNextLines.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13class ScannerNextLines {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("NextLine方式接收:");
// 判断是否还有输入
if (scan.hasNextLine()) {
String str = scan.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入的数据为:" + str);
}
scan.close();
}
}
注意:如果要输入 int 或 float 类型的数据,在 Scanner 类中也有支持,但是在输入之前最好先使用 hasNextXxx() 方法进行验证,再使用 nextXxx() 来读取。
- ScannerNumbers.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34public class ScannerNumbers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int numberI;
float numberF;
double numberD;
System.out.println("输入整数:");
if (scan.hasNextInt()) {
numberI = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("整数是:" + numberI);
} else {
System.out.println("输入的不是整数!");
}
System.out.println("输入浮点数:");
if (scan.hasNextFloat()) {
numberF = scan.nextFloat();
System.out.println("浮点数是:" + numberF);
} else {
System.out.println("输入的不是浮点数!");
}
System.out.println("输入双精度小数:");
if (scan.hasNextDouble()) {
numberD = scan.nextDouble();
System.out.println("双精度小数是:" + numberD);
} else {
System.out.println("输入的不是双精度小数!");
}
scan.close();
}
}
11,Java异常处理
1)理解Java异常处理是如何工作的,需掌握以下三种类型的异常:
检查性异常:最具代表的检查性异常是用户错误或问题引起的异常,这是程序员无法预见的。运行时异常: 运行时异常是可能被程序员避免的异常。与检查性异常相反,运行时异常可以在编译时被忽略。错误: 错误不是异常,而是脱离程序员控制的问题。错误在代码中通常被忽略。
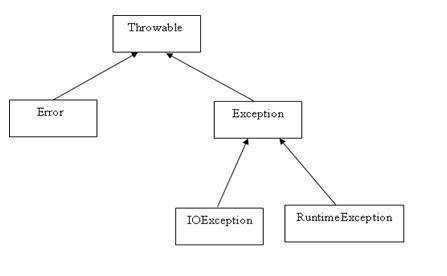
2)Exception 类的层次
- 所有的异常类是从
java.lang.Exception类继承的子类。Exception类是Throwable类的子类。除了Exception类外,Throwable类还有一个子类Error。Error用来指示运行时环境发生的错误。例如,JVM内存溢出。一般地,程序不会从错误中恢复。- 异常类有两个主要的子类:
IOException类和RuntimeException类。- 在 Java 内置类中,有大部分常用
检查性和非检查性异常。
3)Java内置类
4)异常方法:主要是Throwable的方法。
5)捕获异常1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public class ExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] array = new int[2];
array[0] = 1;
System.out.println("Access elements three: " + array[2]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
System.out.println("Exception: " + ex.toString());
}
System.out.println("Out of the block.");
}
}
6)多重捕获块:一个 try 代码块后面跟随多个 catch 代码块的情况就叫多重捕获。
7)throws/throw关键字:如果一个方法没有捕获到一个检查性异常,那么该方法必须使用 throws 关键字来声明。throws 关键字放在方法签名的尾部。
8)finally关键字:finally 关键字用来创建在 try 代码块后面执行的代码块;无论是否发生异常,finally 代码块中的代码总会被执行;在 finally 代码块中,可以运行清理类型等收尾善后性质的语句。
- ExceptionDemo.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public class ExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[2];
try {
System.out.println("Access elements three: " + array[2]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
System.out.println("Exception throw: " + ex.toString());
} finally {
array[0] = 20;
System.out.println("First element value: " + array[0]);
System.out.println("The finally statement is executed.");
}
}
}
9)声明自定义异常
- 所有异常都必须是 Throwable 的子类。
- 如写一个检查性异常类,则需要继承 Exception 类。
- 如写一个运行时异常类,那么需要继承 RuntimeException 类。
综合实例
InsufficientFundException.java:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12/**
* 自定义异常,继承Exception类
*/
public class InsufficientFundException extends Exception {
private double amount;
public InsufficientFundException(double amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public double getAmount() {
return amount;
}
}CheckingAccount.java:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35/**
* 银行账户基本操作类
*/
public class CheckingAccount {
private double balance;
private int number;
public CheckingAccount(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
// 存钱
public void deposit(double amount) {
balance += amount;
}
// 取钱
public void withdraw(double amount) throws InsufficientFundException {
if (amount <= balance) {
balance -= amount;
} else {
double needs = amount - balance;
throw new InsufficientFundException(needs);
}
}
// 返回余额
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
// 返回账号
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
}BankDemo.java:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21**
* 模拟银行账户基本操作实例
*/
class BankDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CheckingAccount account = new CheckingAccount(6228481);
System.out.println("Deposit $500...");
account.deposit(500.00);
try {
System.out.println("Withdrawing $100...");
account.withdraw(100);
System.out.println("Withdrawing $600...");
account.withdraw(600);
} catch (InsufficientFundException ex) {
System.out.println("Sorry, but you are short $"+ex.getAmount());
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
10)通用异常
在Java中定义了两种类型的异常和错误:
JVM(Java虚拟机) 异常:由JVM抛出的异常或错误。例如:NullPointerException类,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException类,ClassCastException类。- 程序级异常:由程序或者API程序抛出的异常。例如
IllegalArgumentException类,IllegalStateException类。